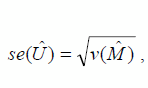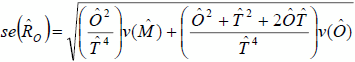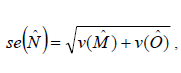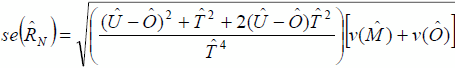Common menu bar links
 View the most recent version.
View the most recent version.Archived Content
Information identified as archived is provided for reference, research or recordkeeping purposes. It is not subject to the Government of Canada Web Standards and has not been altered or updated since it was archived. Please contact us to request a format other than those available.
9. Estimation
Estimation for the DCS, RRC, and the COS are covered in Section 6.2, Section 7.4, and Section 8.3 respectively. This section describes how the results of the census coverage studies are combined to produce estimates of census population undercoverage (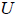 ), population overcoverage (
), population overcoverage (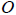 ), and population net undercoverage (
), and population net undercoverage (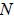 ) for a variety of domains. The impact of sampling error on the quality of the estimates is also produced by calculating an estimated standard error for each estimate. The results of the Reverse Record Check (RRC) and census data are used to construct estimates of undercoverage while the results of the Census Overcoverage Survey (COS) provide estimates of overcoverage. Net undercoverage is the difference between undercoverage and overcoverage. This section details the calculation of these estimates and their estimated standard errors.
) for a variety of domains. The impact of sampling error on the quality of the estimates is also produced by calculating an estimated standard error for each estimate. The results of the Reverse Record Check (RRC) and census data are used to construct estimates of undercoverage while the results of the Census Overcoverage Survey (COS) provide estimates of overcoverage. Net undercoverage is the difference between undercoverage and overcoverage. This section details the calculation of these estimates and their estimated standard errors.
Let:
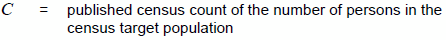
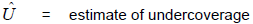
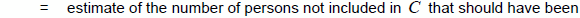


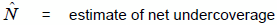
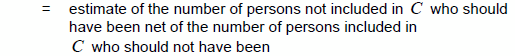
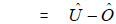
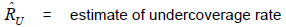

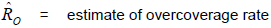
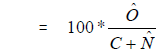

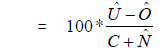
The estimate of overcoverage from the COS is constructed by summing the weights for each person found to be involved in more than one enumeration. If, for example, a case of overcoverage involving two enumerations is found in Step 1 of the COS, then each enumeration receives a weight of ½. Assuming that overcoverage other than from multiple enumerations, such as enumeration of fictitious persons, is negligible, then:
If 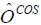 = estimate of overcoverage from the COS, then
= estimate of overcoverage from the COS, then 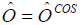 .
.
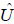 is constructed from the results of the RRC and census data as follows.
is constructed from the results of the RRC and census data as follows.
Let:

![]()
Then 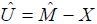 .
.
 , for database extractions, can be determined from the final census database. Persons in the RRC sample (SPs) who are in scope for the census, but for whom the RRC cannot determine whether or not they have been enumerated at their Census Day address, are classified as Missed. There are a number of reasons why an SP could not be identified as enumerated:
, for database extractions, can be determined from the final census database. Persons in the RRC sample (SPs) who are in scope for the census, but for whom the RRC cannot determine whether or not they have been enumerated at their Census Day address, are classified as Missed. There are a number of reasons why an SP could not be identified as enumerated:
- The SP's Census Day address points to a dwelling that contains imputed enumerations. This is the case, for example, for non-response dwellings for which the data of another household was used as a result of whole-household imputation (WHI).
- Some enumerations on the census database were deemed too incomplete to be used by the RRC to identify an SP as enumerated. Incomplete enumerations in this context usually involve invalid data in the date of birth or the name field such as a name of '?' or 'Mr.' or 'Unknown' or 'Person 1.' Any SP pointing to such an enumeration was classified as missed. These are the 'RRC incomplete enumerations.'
- There were some enumerations added to the census database after the data were extracted to create the RRC database. These late enumerations were not available to the RRC so the RRC could not identify any enumeration at these dwellings.
At the national level,  is about half of
is about half of 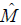 . This is a notable increase from 2001 when X was only about ⅓ of
. This is a notable increase from 2001 when X was only about ⅓ of 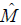 . The increase is largely due to an increase in both the number of non‑response dwellings and the number of misclassified dwellings that resulted in doubling the number of persons imputed during the WHI step of census processing. The following table gives the components of the estimated population coverage error for Canada.
. The increase is largely due to an increase in both the number of non‑response dwellings and the number of misclassified dwellings that resulted in doubling the number of persons imputed during the WHI step of census processing. The following table gives the components of the estimated population coverage error for Canada.
The estimated standard errors are defined as follows:
Let:
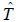 = estimate of the number of persons in the census target population derived from the census count and the estimate of net population undercoverage
= estimate of the number of persons in the census target population derived from the census count and the estimate of net population undercoverage
= ![]()
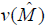 = estimated variance of
= estimated variance of 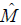 as determined by the design of the RRC
as determined by the design of the RRC
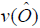 = estimated variance of
= estimated variance of 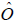 as determined by the design of the COS
as determined by the design of the COS
Then,